
Welding fume is a known carcinogen that can lead to lung cancer, according to the International Association for Research on Cancer (IARC).
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) Impact on health
IMPORTANCE OF AIR FILTRATION
The effects of particulate matter on human health have been extensively studied in the past. The results are that fine dust can be a serious health hazard. The most important diseases which have been associated with (caused or aggravated by) indoor air exposures due to PM contamination are:
- Allergy & Asthma
- Lung cancer
- Cardiovascular diseases (CVD)
- Chronic obstructive lung disease (COPD)
- Dementia
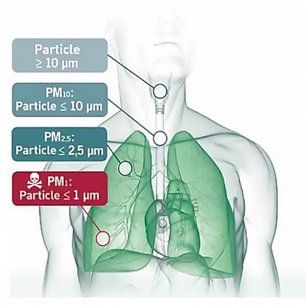
Moreover, there is good evidence of the effects of exposure to various particle size ranges:
Published at the end of 2016, the new EN ISO 16890 standard has established an efficiency classification system of air filters for general ventilation based upon particulate matter (PM). This new classification introducing efficiency for various particle size ranges (ePM 1, ePM2,5, ePM10) provides completely new, so far unavailable opportunities for designing Indoor Air Quality (IAQ). Yet, it differs considerably from the old classification defined in the well-known and commonly applied EN 779 standard.
- PM10: Particles 10 µm in diameter or smaller can reach the respiratory ducts and potentially cause decreased lung function.
- PM2.5: Particles 2.5 µm in diameter or smaller can penetrate the lungs and cause decreased lung function, skin and eye problems.
- PM1: Particles 1 µm in diameter or smaller are most dangerous. They are tiny enough to enter the bloodstream and lead to cancer, cardiovascular diseases and dementia.
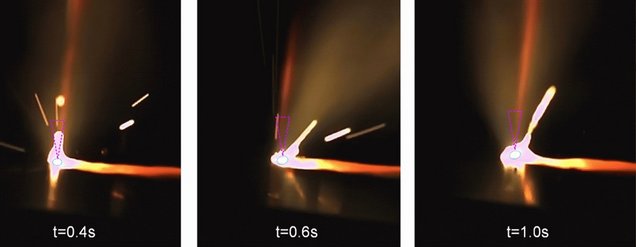
Although invisible for the human eye, there is a fume creation which can influence our health
Infra red picture of the laser welding beam creating invisible fume
Ventilation Solutions for Laser Welding
Why direct capture of the laser Welding fumes on the welding spot?
Laser welding is a rapidly growing process in manufacturing and is popular due to its high level of precision and efficiency. While the initial investment for laser welding systems is higher than most other systems, the benefits are profound in terms of ability and speed. However, laser welding operations incur serious challenges when it comes to weld fumes.
Because laser welders operate at such high temperatures, their weld fumes are full of very small particulates. The smaller the particulate, the more inhalable and dangerous it is for workers.
While an fully automatic laser welding machine/robot functions in an enclosed cell—one without a human operator—it is still very important to capture the fumes inside the cell. Source capture by Flexible vacuum tubes by or enclosing hoods are the most effective in controlling contaminants at handheld laser welding
When Laser welding with a handheld laser welding machine, it becomes even more important to capture the fumes and microscopic dust before the welder can inhale. Therefor every welding cell for manual welding should have a fume filtering system directly on the welding action place.
Besides toxicity and other reasons to collect weld fumes, such as safety regulations, laser welders need a fume free environment so the laser can perform at its optimal level. If fume builds up near the laser, the particles within the fume can refract the laser beam, making the process both less efficient and less precise.
Source capture is the most effective in controlling contaminating welding fume!
Because source fume capture does remove fume at the source, it does limit immediate exposure at the worker’s breathing zone.
ENERGY EFFICIENCY OF FILTERS
A substantial feature of the air filter, besides the efficiency of particle separation, is its flow resistance which directly translates into an energy consumption. This parame- ter plays an increasingly important role.
Due to rising Ecodesign requirements for ventilation equipment, pressure drop over filters pertains a significant share of the overall pressure drop in HVAC systems. It has a crucial impact on the total energy consumed by mechanical ventilation. Energy efficiency links the amount of energy required (effort) to the particle filtration efficiency of the filter (benefit). Understanding this energy efficiency is even more relevant when acknowledging that many end users are not aware of differences in energy consumption related to various filters offering an equal filtration efficiency performance.

